Monitoring for proteinuria in patients receiving bevacizumabMonitoring for proteinuria in patients receiving bevacizumab
Editor's comments
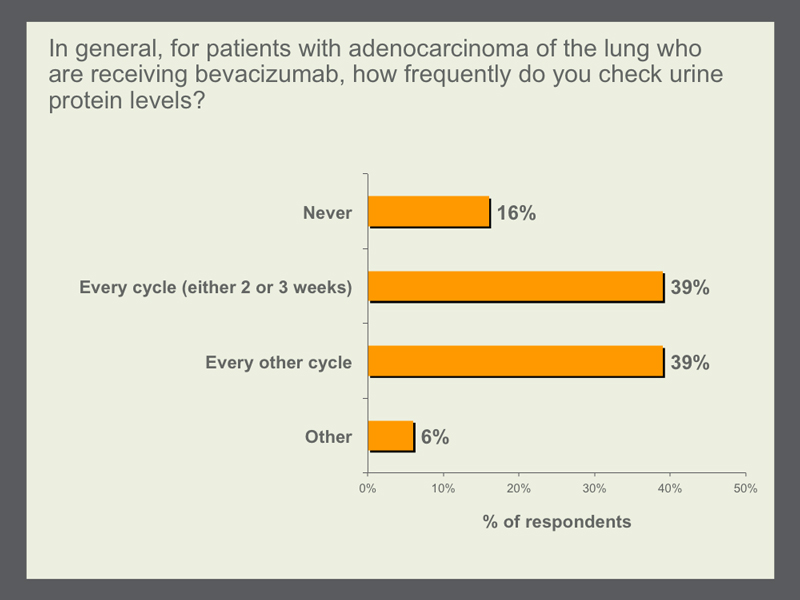
Although the exact mechanism of action and reasons why are not fully understood, it is widely appreciated that treatment with bevacizumab increases the risk of severe proteinuria. As such, adequate and timely detection is necessary to properly intervene, although it is interesting that oncologists are split as to whether monitoring should take place after every cycle or every other cycle. Both faculty members opt for the latter approach and are unified in their belief that evaluating urine protein is absolutely necessary because, as Dr Ramalingam puts it, “having a patient with frank nephrotic-range proteinuria that continues on bevacizumab could be bad in a number of ways.” |