Calcium and magnesium for oxaliplatin-induced neuropathyCalcium and magnesium for oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy
Editor's comments
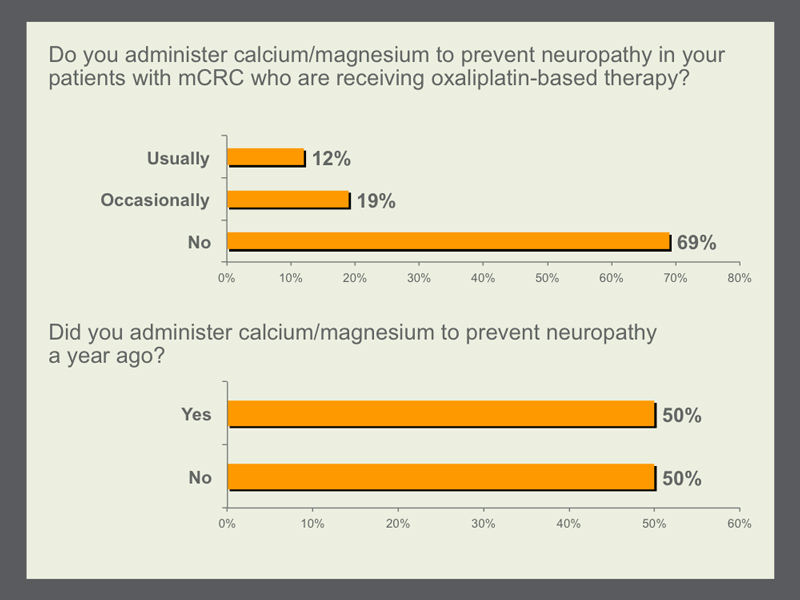
Peripheral neuropathy is a key clinical factor in longer-term treatment with oxaliplatin and one that usually limits the duration of therapy. The hope that preemptive calcium and magnesium administration could prevent or ameliorate this important problem was crushed at the 2013 ASCO Annual Meeting when the report of a definitive placebo-controlled study from the Mayo Clinic demonstrated no effect of this intervention. Although half of the GOs and both faculty members were using this strategy before the presentation of data from this trial, it is now rarely employed, which provides an excellent example of how clinical research findings can be effectively and rapidly translated into practice. |